Astra, the fastest privately-funded company in history to demonstrate orbital launch capability, and Holicity Inc. (NASDAQ: HOL), a special purpose acquisition company (“SPAC”), announced a definitive business combination agreement that will result in Astra stock becoming a publicly traded company. The transaction is estimated to be completed in Q2 2021, and the combined company will trade under the Nasdaq ticker symbol ASTR.
Astra has booked over $150 million of contracted launch revenue. Astra will begin delivering customer payloads this summer and begin monthly launches by the end of this year. Morgan Stanley’s Space Team estimates that the roughly $350 billion global space industry could surge to over $1 trillion by 2040.
Astra Company background
Chris Kemp is the Chairman, Founder and CEO. He previously served as CTO of NASA and founded OpenStack. He also developed the Cloud computing strategy for the United States Government at White House. Adam London is the Founder and CTO.He founded Ventions and spent the majority of his career inventing miniature rocket technologies in partnership with NASA and DARPA.

Astra manufacturing facility
The company has its headquarters at the Alameda Naval Air Station just outside of San Francisco. It is turning the facility into the world’s first fully integrated rocket development, manufacturing, and test facility. The rockets are built iteratively using software design principles. The company has an extensive software stack. It plans everything from sourcing materials, powering the facility, performing tests, and modifications to design from this software platform. There is no need to go to a desert to test out its components.
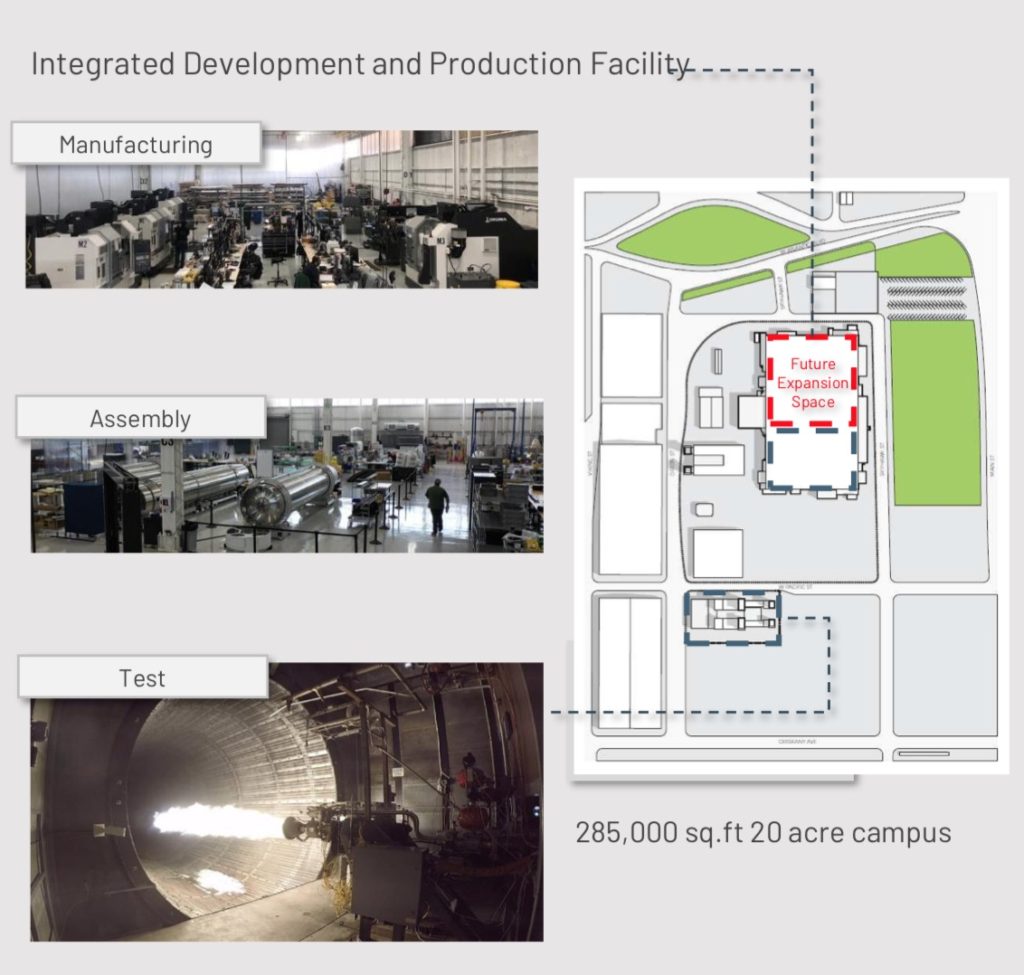
Because of this speed of execution, the company was able to launch a satellite in orbit in just 4 years timeframe beating SpaceX and Rocket Lab. Rapid test and iteration are the cornerstones of the development process. The company performed thousands of rocket engine tests a few hundred feet away from where those engines are designed and built. This is possible because the rockets are far less expensive. They are constructed from lightweight aluminum, instead of costly composite and 3D printed materials.
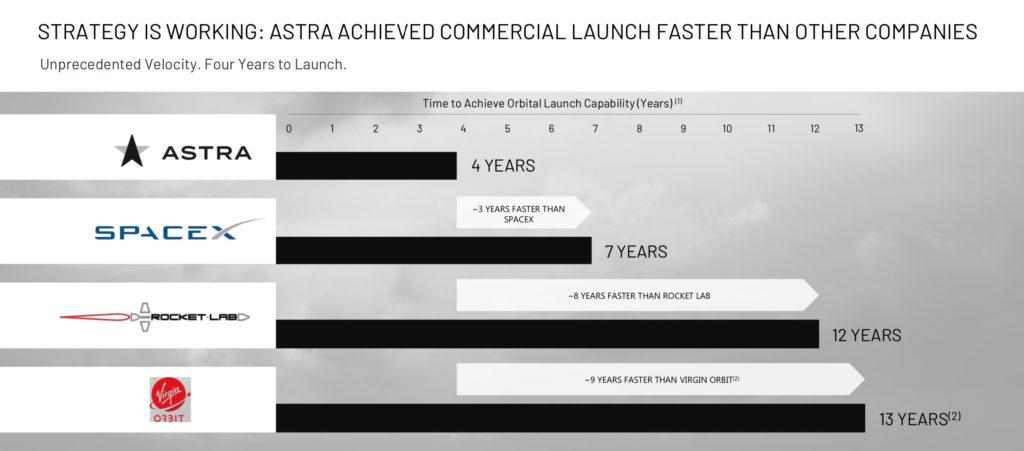
Astra key highlights
- 10+ customers and 50+ launches in the backlog.
- Astra has $150+ million in contracted revenue.
- The company has 100 spacecraft in its backlog.
- All customers are highly reputable, well-funded and currently in orbital operation
- The company was awarded a NASA Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) contract for the launch of NASA CubeSats. Astra will carry out three launches in 2022 to deliver NASA CubeSat satellites that will allow scientists to better measure the temperature, pressure and humidity of hurricanes.
- The time to build the new Kodiak spaceport: is ~6 months. The company has 10+ launch Sites identified around the world. The commercial FAA spaceports only require concrete pads.
- The company is looking for daily launch capability. Booking a launch will be as easy as booking an airline ticket. This will remove delays for the constellation players as they no longer have to face delays due to infrequent launch schedules of larger rockets.
- 3 revenue streams – launch, spacecraft platforms, and spaceport services.
- World-class management team with unparalleled industry experience at NASA and SpaceX.
DARPA launch challenge winner
The goal of the DARPA Launch Challenge is to demonstrate responsive and flexible space launch capabilities from the burgeoning industry of small launch providers. For nearly 60 years, the nation’s space architecture has been built around exquisite systems that are launched by large, expensive boosters. The development cycle with the systems is tedious, with a process driven by a desire to reduce risk, rather than deliver timely capabilities.
The DARPA Launch Challenge seeks to demonstrate new and groundbreaking capabilities to address emerging Department of Defense needs. The challenge will culminate in two separate launch competitions to low Earth orbit (LEO) within days of each other at different locations in the United States.
Astra was the sole competitor after Virgin Orbit and Vector Launch eventually dropped out. It came very close to winning the competition but the second launch was not completely successful due to some fuel problem. However Astra achieved all its objectives and established itself on the stage.
Merger Transaction Details
- Fully diluted pro forma enterprise value of $2.1B, representing 3.1x based on 2025E adjusted EBITDA of $694M.
- Transaction will result in $489M of cash to the balance sheet to fund growth.
- Transaction includes $300 million of cash held in trust and $200 million PIPE.
- The deal is expected to close by the second half of 2021.
- HOL ticker symbol will change to ASTR upon closing and listed on the Nasdaq.
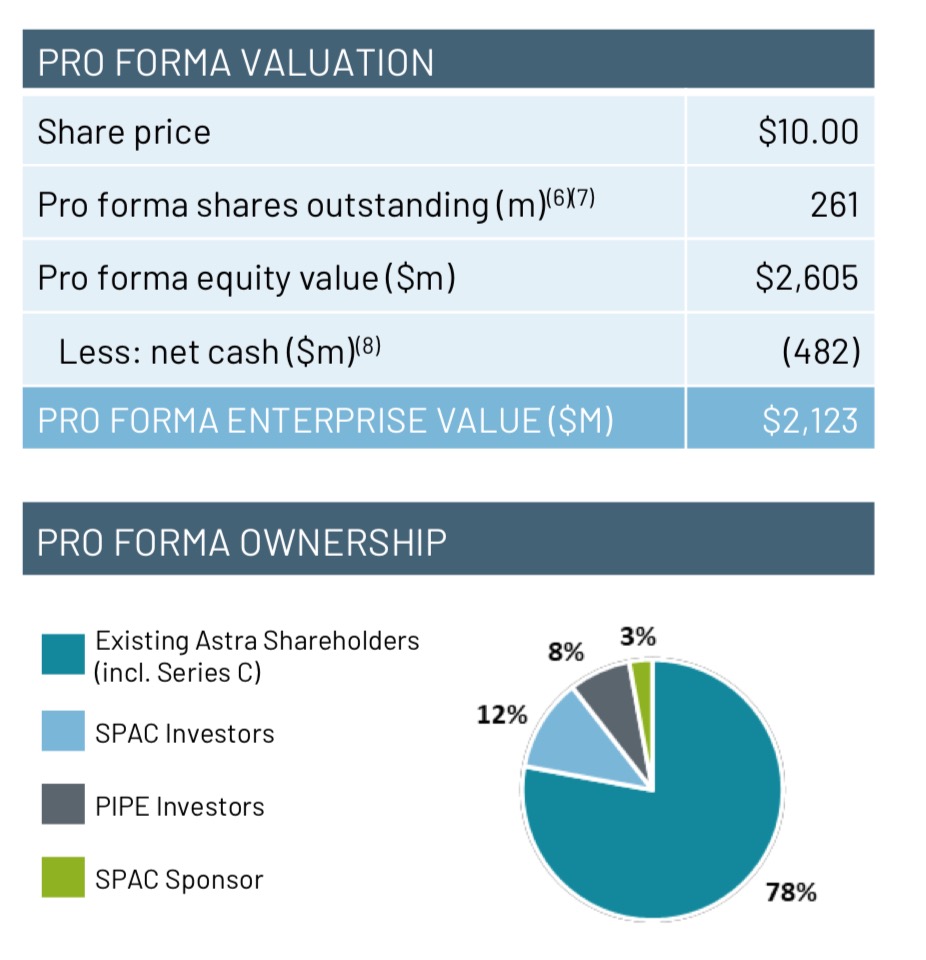
Astra stock share structure
- Total shares outstanding of approximately 261 million.
- 78% existing Astra shareholders.
- 8% PIPE investors.
- 12% HOL SPAC shareholders.
- 3% SPAC sponsors.
Astra Stock Valuation
- The high-growth space applications market that comprises approximately $320 billion of the current $350+ billion space industry TAM.
- The global space market is forecast to grow to $1.4T by 2040.
- The company is aiming for daily launch capability. There are 3 revenue streams – launch, spacecraft platforms, and spaceport services
- 1.2B in pipeline revenue. 10+ customers and 50+ launches in the backlog.
- Over $150+ million in contracted revenue.
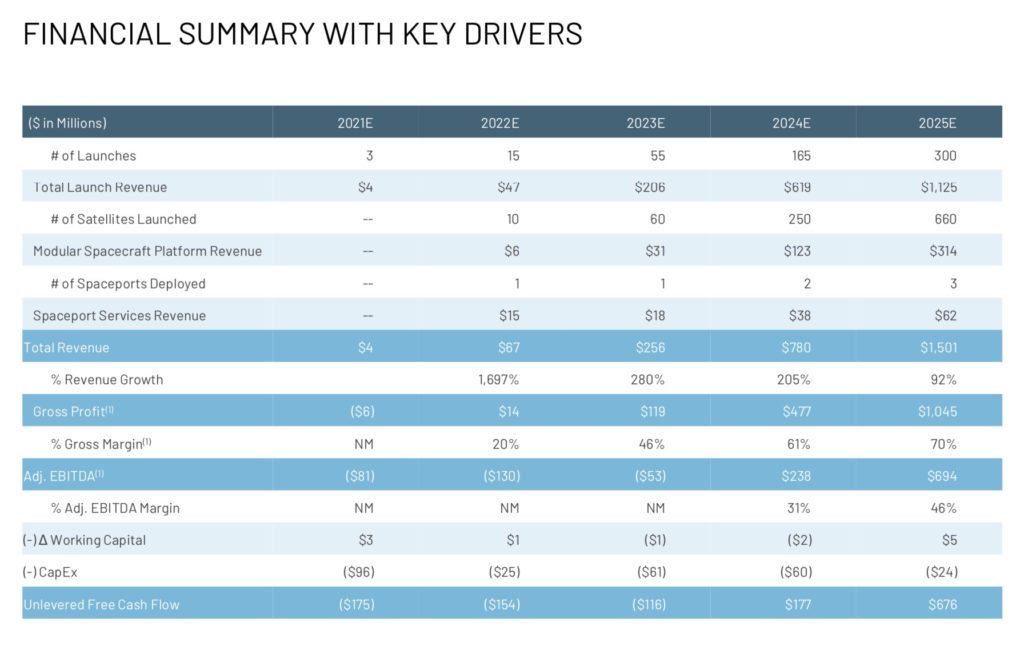
Management Valuation for 2025
- $1.5 billion revenue and an EBITDA of $694 million by the end of 2025.
- The company is expected to be cash flow positive by 2024 with $177 million FCF.
- Valuation multiple of EV/EBITDA of 10. That gives an EV of $6.94 billion.
- Divide $6.94 billion EV by the 261 million Shares outstanding. This gives a valuation of $26.50 per share in 2025 estimated.
Risk Factors
- The real meat of the revenue in the space market is in space applications. The TAM for the analytics market is expected to be $320 billion. Using the data from constellations to develop analytics and intelligent insights for customers. Astra like Rocket Lab does not have an analytics solution for space applications nor does it own any proprietary space data.
- The company does not have a reusable first stage rocket. Its rockets are cheap and the kickoff stage rockets linger in space. This may cause space debris and may be a concern for the long run.
- The launch sites are yet to be built out. The company has identified 10 launch ports across various locations in the world. In order to build the ports, various clearances and permits would be required. Especially for overseas ports.
- Astra has no plans yet for large satellite launches and deep space missions. It is focusing its business on launching only small constellations. There are other players in the market. By the time the company gets to the schedule of daily launches, a lot of market partnerships may be covered by other companies as well.

